This paid content has been provided by a third party and does not necessarily represent the views or opinion of FlightGlobal
Every day, millions of people fly. Each flight from the airport is ensured by automated systems taking care of dozens of processes – from baggage sorting to air traffic control. Jet refueling is one of these processes, and everyone expects it to be as quick and safe as possible.
Today, refueling is going through a transformation with technologies playing a key part.
A special working group that includes air carriers, fuel suppliers and service providers was created at IATA. The Fuel Data Standards Group (FDSG) expert group sets new standards for data exchange in the international aviation industry based on the universal digital XML* digital standard.
Standardization covers all the most important stages of the refueling process: from tendering to invoicing. For instance, the aviation fuel operator Gazpromneft-Aero joined FDSG with its own developments in data transfer processes and took a leading role in the introduction of IATA standards in Russia.
- Tender - XML Fuel Tender Standard
- Refueling Application - XML Fuel Operational Standard
- Expense voucher - XML Fuel Transaction Standard
- Account - XML Fuel Invoice Standard
Each of these four XML standards is designed to accelerate data exchange, reduce the possibility of errors in manual paperwork and increase the efficiency of aircraft refueling.
In 2019, Gazpromneft-Aero, was among several companies (e.g. Air France, Lufthansa, Finnair, Cathay Pacific) that tested a data transfer system for refueling using the IATA XML Fuel Operational Standard in conjunction with a proof of concept data hub developed by IATA.

The goal is to build a global industry platform will reduce airlines’ costs for data transfer to dozens of airports and increase data reliability.
Gazpromneft-Aero has also started the digital transformation of its own refueling facilities and services, laying the groundwork for technological leadership in the international aviation fuel market.
An electronic system for refueling operations will allow to plan and control aircraft handling at an airport apron. After receiving a fueling request from the airline, the system will process data from the control tower such as flight number, parking stand number and scheduled refueling time. This information is then automatically displayed on a tanker driver’s tablet.
Refueling trucks are additionally equipped with a controller, an electronic display, a mass meter, a GSM module and a printer. The operation algorithm will allow the wingman to reduce the time spent on paper documentation and to eliminate accounting errors.
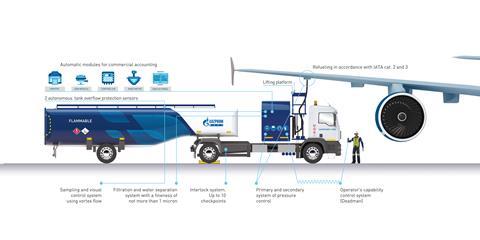
To start working with the controller, an operator must log in using a smart card, then enter data on the required amount of fuel and additives. All the information on refueling parameters is shown online on the controller system display. Once the necessary amount of fuel is uplifted to the aircraft, the system automatically stops the process, prints a document, and then sends a refueling report to the Gazpromneft-Aero’s server and to the airline using the GSM module. Thanks to digital technologies, the operator is practically immune to calculation errors in determining the mass of fuel delivered and filling out the primary documentation after refueling the aircraft.
The long-term goal of the company is to introduce effective digital control of all of the operational fuel processes with almost no human involvement.
* XML is extensible markup language. XML-based files, which are widespread, store a wide variety of data, from application settings to business data. XML-based files are used to exchange information on the Internet and between computer programs (which was the initial goal of this markup language). As long as XML files contain text data, they can be easily edited in any text editor. The use of XML in data exchange is recognized as the least expensive and most accessible format for the exchange of information among market participants.

























